Xanax is a known anti-anxiety medication popular in United States, United Kingdom, and all across the world. The medicine is benzodiazepine, Alprazolam which people use to treat anxiety and panic disorders. It is one of the most generally prescribed psychiatric medicines across the globe. Here, you will get to know about the uses of Xanax, how to take it properly, its potential side effects, and the warnings associated with Xanax use.
What is Xanax?
Xanax is Alprazolam, an anti-anxiety medicine in the class of benzodiazepine medications. The family of benzodiazepines also contain some other famous anxiety medicine, including Lorazepam, Clonazepam, Diazepam, and Flurazepam.
The medicine is a centrally acting agent that works by decreasing abnormal excitement in your brain. It acts on the brain and the central nervous system to produce a relaxing or calming effect. The United States Food and Drug Administration approved Alprazolam for medical use in October 1981.
Xanax usually acts to slow down the movement of brain chemicals or neurotransmitters that may become unbalanced in a person with anxiety and tension. The medicine boosts the effects of a natural neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid.
Xanax Uses
Doctors prescribe Xanax to manage anxiety or provide relief from anxiety disorder symptoms. Tension or anxiety associated with everyday life stress usually does not require treatment with medications like Xanax.
Generalized anxiety disorder is responsive to Xanax. It is the unrealistic or excessive worry or anxiety about some life situations for a period of more than 6 months. During this time, the person remains bothered about different life circumstances.
More than six of the following symptoms are present in people with generalized anxiety disorder:
- Autonomic hyperactivity, including shortness of breath, heart palpitations, sweating or cold or clammy hands, dry mouth, lightheadedness or dizziness, nausea, diarrhea, frequent urination, hot flashes or chills, and difficulty swallowing.
- Motor tension, including twitching, trembling, muscle tension, feeling shaky, restlessness, soreness or aches, and feeling easily tired.
- Scanning and vigilance, including feeling on the edge or keyed-up, irritability, difficulty falling or staying asleep, exaggerated startle response, and difficulty concentration because of anxiety.
Another primary Xanax use is to treat panic disorder, caused with or without agoraphobia. The medicine may also reduce the frequency of panic attacks a person has.
Panic disorder is having regular panic attacks for relatively short periods of unrealistic and intense fear with four or more of the following physical and mental symptoms developed quickly and reached a peak within 10 minutes:
- Sweating
- Heart palpitations
- Shaking or trembling
- A feeling of choking
- Chest discomfort or pain
- Shortness of breath or smothering
- Nausea or abdominal distress
- Fear of losing control or dying
- Feeling unsteady, dizzy, faint, or lightheaded
- Hot flashes or chills
Xanax Dosage
Xanax pills are available as a conventional tablet, an extended-release tablet, a concentrated solution, and an orally disintegrating tablet, one that dissolves quickly in the mouth. A person should take Xanax pills by mouth as directed by a doctor. Xanax dosage is usually based upon the following factors:
- The condition for which a person is taking Xanax
- Their age, health, and other conditions
- How their body responds to the treatment
Your doctor may gradually decrease Xanax dosage until the medicine works effectively for you. You should closely follow the instructions of your doctor to reduce the risks of adverse effects.
In case you are using Xanax pills regularly for a long period of time or at a higher dose, withdrawal symptoms may occur if you abruptly stop taking this medicine. To prevent Xanax withdrawal symptoms, a doctor will gradually reduce the dosage.
Xanax immediate-release tablets are available in the following doses of Alprazolam:
- Xanax 0.25mg: these are usually white, oval-shaped, scored, and imprinted pills with “XANAX 0.25” written on it.
- Xanax 0.5mg: these are usually peach, oval-shaped, scored, and imprinted pills with “XANAX 0.5” written on it.
- Xanax 1mg: these are usually blue, oval-shaped, scored, and imprinted pills with “XANAX 1.0” written on it.
- Xanax 2mg: these are usually white, green, blue, or yellow, rectangular-shaped, scored, and imprinted pills with “XANAX” written on one side and “2” other. Xanax 2mg pills are known as Xanax bars due to their shape of a rectangular bar.
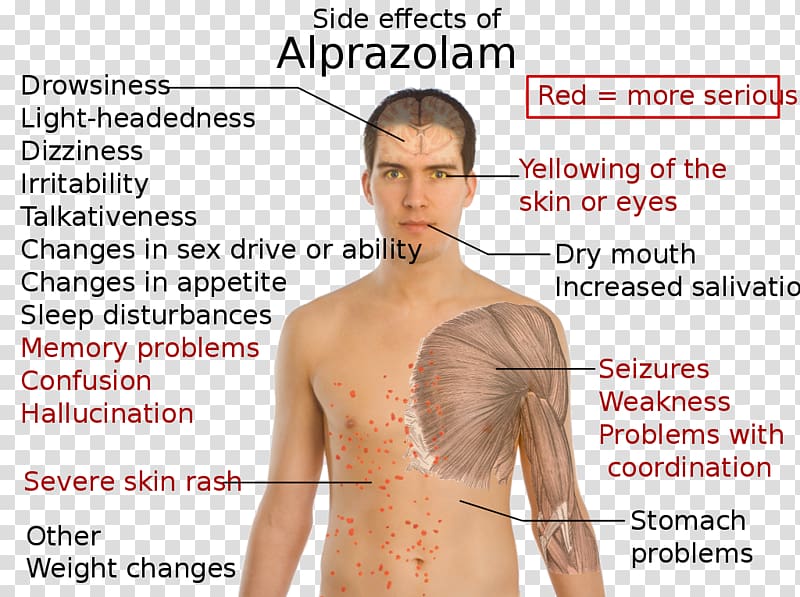
Xanax Side Effects
Most of the Xanax side effects usually occur when beginning the treatment and generally subside within several days of use. Some potential side effects of Xanax include:
- Low energy
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Lightheadedness
- Headache
- Confusion
- Fainting
- Nervousness
- Insomnia
Other effects include depression, impaired coordination, restlessness, irritability, decreased libido, abnormal involuntary movement, muscle cramps and twitching, constipation or diarrhea, skin rash, nausea or vomiting, hyperventilation, hypotension, blurred vision, menstrual disorder, abnormal dreams, edema, weight loss or gain, incontinence, and slurred speech.
These are only mild to moderate side effects of Xanax that generally do not require medical attention. However, the medication may also cause severe adverse effects when abused or not used properly as prescribed.
Allergic reactions caused due to Xanax use include hives, trouble breathing, and swelling of several parts of the face, including lips or tongue and throat.
Severe Xanax side effects include:
- Suicidal thoughts, severe depression, risk-taking behaviors, and decreased inhibitions
- Feeling or getting faint
- Hyperactivity, confusion, hostility, agitation, or hallucinations
- Chest pain, racing heartbeat, fluttering feeling in the chest
- Jaundice or yellowing of eyes or skin
- Uncontrolled muscle movements, seizures, or tremors
Warnings
Certain warnings are associated with Xanax to ensure the safe and effective use of the medication. A doctor will provide these Xanax warnings along with the prescription:
- You should inform the doctor about alcohol consumption and any medicine you are currently taking, such as over-the-counter medicines. People should not take Xanax and alcohol together.
- Doctors recommend that pregnant ladies not use Xanax as this medicine poses a risk to the fetus. Also, breastfeeding women should refrain from taking Xanax pills as they can pass through the breast milk, causing withdrawal symptoms in the nursing baby.
- Until you know how Alprazolam affects your brain, do not drive any vehicle, operate or lift any heavy machinery, or do any other work that requires mental alertness to avoid the risks of accidents and falls.
- Increasing or decreasing Xanax dose without speaking to a doctor can be dangerous and produce physical or mental dependence or tolerance.
- Inform your doctor in case you have any of the specified conditions: asthma or breathing problems, liver diseases, glaucoma, suicidal thoughts, a history of depression or alcohol abuse, or substance use disorder.
- Several medical conditions contraindicate Xanax use. These include narrow-angle glaucoma, depressive or suicidal thoughts or attempts, kidney or liver diseases, and several other conditions.
- People should not take several medicines while on Xanax treatment as they can interact, causing unwanted effects. Significant Xanax interactions include ketoconazole, itraconazole, and others.